Manganese-silicon flux (MS), Fuse Flux (F) is a welding wire. for welding non-alloyed steel and low alloy steel which has no addition and loss of important compound elements In addition to carbon.
udo.co.th The equipment center, grinding machines, grinding wheels and various tools for welding work of all kinds. We have a team of highly experienced professionals to give advice and consultation to all customers.
Silicon and manganese (class 1), sitigon has a gain of not more than 0.39 by weight (6) and no gain or loss of element (5). It is suitable for AC welding. ) Good weldability with filet welds (K)
2.2 Flux for welding alloy steel
Flux Type Aluminum Basic (AB) , Bonded Flux (B) does not contain chromium as the main ingredient. For welding stainless steel and heat-resistant steel (quality class that 6 gain no more than 0.3% by weight of silicon (6), 0.3-0.5% by weight of manganese loss (3), dromium loss of more than 0.7% by weight (1), niobium loss between 0: 0.5% by weight (3) suitable for welding with direct current (DC) with a current size of 700 A (1) especially suitable for welding reinforced strips (B).
The original standard for welding mild steel gas (JIS Z 3201-1990)
This Japanese industrial standard requires gas filling wire. Used for welding carbon steel and similar metals.
1. Type of wire used for gas welding (Classification)
Gas filling wire can be divided into types. according to the tensile stress and elongation of the weld
2. Fill wire quality
2.1 Characteristics The surface of the gas welding wire must be smooth and free from defects that affect its use.
It has been coated with copper to prevent rust.
2.2 Chemical ingredients When the chemical mixture has been tested The resulting value must be correct.
2.3 Mechanical properties The resulting weld must have mechanical properties.
3. Marking on gas welding filler wire
The filling wire must be clearly marked on the packing box. and must also be marked on the line By specifying with the color code at the end of the wire to make it easy to distinguish.
3.12 Mild steel flux-clad welding wire standard For manual arc welding (SMAW) processes, JIS Z 3211-1991 standard.
Classification of welding mugs based on cladding flux type for proper welding position and current type
welding wire symbol
welding position symbol
F = horizontal , V – vertical , O = overhead line
H = horizontal or horizontal welds
welding position Vertical and overhead lines are not ruled out. when using a larger wire rod
5.0 mm.
Stream type symbol
AC = alternating current
DC(±) = DC current (positive wire and negative wire)
DC(-) = DC power (negative wire connection)
DC(+) = DC power (connection wire to power positive pole)
3.13 Alloy wire standard for mild steel and high strength steel (JIS Z 3312-1993).
This Japanese standard stipulates that the filament for mag welding Used for welding mild steel and high strength steel. with tensile stresses of 490 N/mm² and 590 N/mm²
1. Type of welding wire
Welding wires are classified according to the gas cover, the type of steel used. and chemical ingredients
2. The quality of the welding wire
2.1 The surface of the wire must be smooth. without defects that will have a negative effect on its use
2.2 Chemical composition of wire by testing according to specified standards
2.3 Mechanical properties Tensile stress, Yield Point or 0.2% Proof Stress, elongation and Charpy throttle force of the weld Perform the tests according to the required standards.
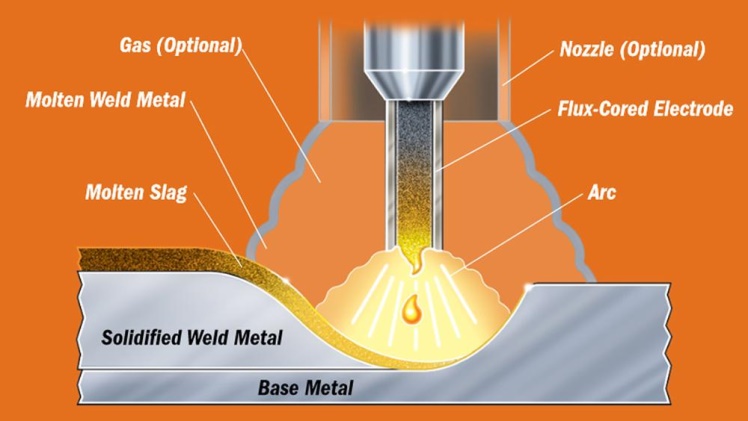
3.14 Flux Cored Wires Standard for Welding Mild Steel, and High Strength Steel (JIS Z 3313-1993)
This Japanese industry standard This wire is specified for use in Gas Shielded and Self-shielded Metal Arc Welding processes for welding mild steel, high strength steel, tensile strength of 490 N/mm 2 and high-strength steel of the tensile strength of 590 N/mm².
3. Type of welding wire
note
(1) welding wire symbol
(2) Cover gas code as follows:
C : Carbon Dioxide , A : Argon and Carbon Dioxide Mixture , S : Cover Gas (Self-shielded Gas)
(3) The minimum tensile strength code of the weld is as follows:
43 : 420 N/mm² 50 : 490 N/mm² 60 : 590 N/mm²
(4) Shows the temperature and energy of the weld impact test.
(5) Type of flux as follows:
R : rutile type , B : alkaline type , M : metal type , G : other types
Rutile type: Flux with rutile (TiO) as the main flux ingredient.
Different types: flux with alkali as the main ingredient of the flux is fluoride.
Metallurgical type: Flux containing metal as the main flux ingredient, i.e. iron powder and alloy powder.
Other types : Fluxes other than type R , B and M
- Welding wire quality
2.1 The appearance of the wire must be smooth and free from defects that are harmful to use.
2.2 Chemical composition of the desired weld
2.3 Mechanical properties such as tensile stress, yield point or 0.2% Proof Stress, elongation and impact test value of the weld required.
3.5 Original TIG welding wire standard for mild steel and low alloy steel (JIS Z 3316-1989).
This Japanese Industrial Standard specifies TIG (Rod and Wire) for welding mild steel, high strength steel, molybdenum steel and chrome-molybdenum steel.
- Type of TIG welding filler wire
Types of wire filling rods (Rod) and coiled wire (Wire)
- Fill wire quality
2.1 Rod and wire must be of consistent quality. have a smooth surface and the skin must be flawless
dangerous to use
2.2 Rod and Wire must be tested for quality according to the specified standards. There must be a chemical mixture.